- Current status and challenges in co-production of sulphuric acid and Portland cement from phosphogypsum
Xiaoling Maa, Hongbin Tana,*, Yassine Tahab, Faqin Dongc, Feihua Yangd, Kaiwen Lia, Zhihong Jianga and Chenggang Xue
aSchool of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China
bMining Environment and Circular Economy, Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, Lot 660, Hay Moulay Rachid, Ben Guerir 43150, Morocco
cKey Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry Education, Mianyang 621010, China
dBeijing Building Materirals Sciences Research Institute Co., Ltd, Beijing 100041, China
eSichuan Diwei Technology Co., Ltd, Mianyang 621010, ChinaThis article is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Phosphogypsum (PG) is a by-product of the wet-process phosphoric acid industry. Co-production process of Portland cement and sulfuric acid from phosphogypsum can realize its resource utilization, sulfur cycle and reduce carbon dioxide emission. The decomposition temperature of gypsum can be reduced using coal as reducing agent, which is beneficial to reduce energy consumption. It will be interesting to produce high-strength-low-calcium Portland (LCP) cement by using phosphogypsum as raw materials. The early strength of the cement can be improved by stabilizing the high temperature structure of dicalcium silicate, changing the hydration environment and adopting carbonation curing. The cement can be manufactured by the equipment of Portland cement industry. The sulfuric acid can be produce with the SO2 flue gases by conventional acid manufacturing process. The CO2 emission is 446.4 Kg per tonne cement by using PG, which can realize sustainable development of phosphorus chemical and cement industry.
Keywords: Phosphogypsum, Precalcining, Sulfuric acid, Low calcium Portland cement, Carbonation curing, CO2 emission.
Phosphogypsum (PG) is a by-product of the wet-process phosphoric acid industry, which gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) is the major component. About 4.5-5 kg of PG is generated for every kg of P2O5 produced. Almost 75 million tons of PG are generated annually in China and its output is estimated to be around 415 million tons worldwide per year [1, 2]. Currently, PG is applied in fields, as soil-stabilization amendments, agricultural fertilizers, cement retarders, building bricks/blocks and cementitious binders, etc. However, the reuse proportion of PG is lower than 10%, while the vast majority of PG is dumped in large stockpiles, which are exposed to weathering processes without any treatment [3]. PG contains metals, organic substances and other potentially toxic elements, which have potential environmental impacts. Therefore, the effective utilization of PG cannot only save the natural gypsum, but protect the environment [4].
Portland cement, the glue of concrete, is the largest manufactured product by human society and the basic ingredient for the construction industry. The cement production is a very important representing index of the infrastructure construction of the society. The CaO in Portland cement clinker is about 65%, which mainly comes from limestone and produces CO2 in the cement manufacturing processes [5-7]. The global cement production reaches to 4.1 gigatons (Gt) in 2018, which consumes about 3 Gt limestone resource [8]. Moreover, it is estimated that by 2050, population growth, urbanization, and infrastructure construction will lead to an increase/upsurge in global cement production. As a result, the cement industry can completely consume the calcium resources in phosphogypsum. The co-production process of sulfuric acid and cement not only utilizes calcium resources from PG, does not discharge solid waste and cuts in carbon emissions, but also produces sulfuric acid for phosphoric acid industry [9]. The process research has gradually become a hot spot in recent years.
As early as 1915, the German Muller first invented the process with coke and natural gypsum as raw materials. And then, Kuhner improved Muller's process and establishes a pilot production line. In 1916, Bayer Fuel Company built the world's first sulfuric acid and cement co-production production line from gypsum by using the Muller-Kuhner process in Leverkusen, Germany. In 1968, Austrian Lunsheng Chemical Company built a production line by using PG as raw material, with a 200 t/d sulfuric acid.
Since the 1950 s, the process had been studied by using natural gypsum and phosphogypsum as materials in China. In the 1960 s, the pilot research had been built. In the 1970 s, the production line of co-production progress was built by using natural gypsum as raw material in Tianjin, Jinan and other places. In 1988, Lubei Chemical Plant built the first demonstration project of 30,000 tons of ammonium phosphate and 40,000 tons of PG to produce sulfuric acid and 60,000 tons cement ("three four six" project).
The industrial equipment of the process ranges from the initial hollow kiln, vertical drum preheater kiln, cyclone preheater kiln, to circulating fluidized bed precalcining kiln, which precalcining equipment can reduce 30% energy consumption. But the co-production process is not widely applied in the world industry. The possible reasons are that the composition is complex and the water content is high in PG, the mechanism of PG decomposition and clinker mineral formation lack systematic research. As a result, the high quality of sulfuric acid and cement are not produced and the energy consumption is high.
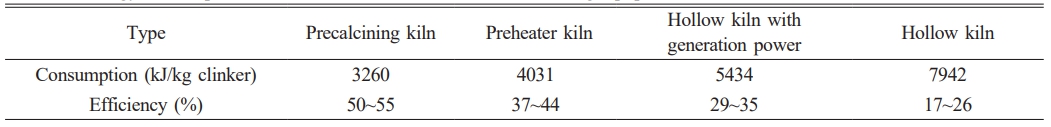
On the other hand, Energy consumption level of different Portland cement calcining equipments is shown in Table 1. The best available technology, the one with the lowest energy consumption, for the cement manufacturing from limestone feed today, is the use of a rotary kiln together with multi-stage cyclone preheater system and a calciner [10]. The production of clinker from limestone feed is shown in Fig. 1. The cyclone preheating systems have been developed to enhance the heat exchange between the raw material and the flue gases. Raw material is heated by moving counter to the flow of the hot flue gases coming from the pre-calciner and rotary kiln. After preheating, raw material enters the pre-calciner, which is a combustion unit found prior to the rotary kiln, and inside of it, the raw material, mainly composed of limestone, undergoes the calcination process. A decrease of energy consumption by 8-11% can be achieved when a rotary kiln is used together with a calciner. This decrease is due to the fact that pre-calciner has lower operating temperature (~850 ℃) than rotary kiln (~1450 ℃).
According to limestone pre-calcining technology in Portland cement industry, the decomposition of gypsum is carried out in the calciner outside the kiln, which is beneficial to reduce energy consumption.
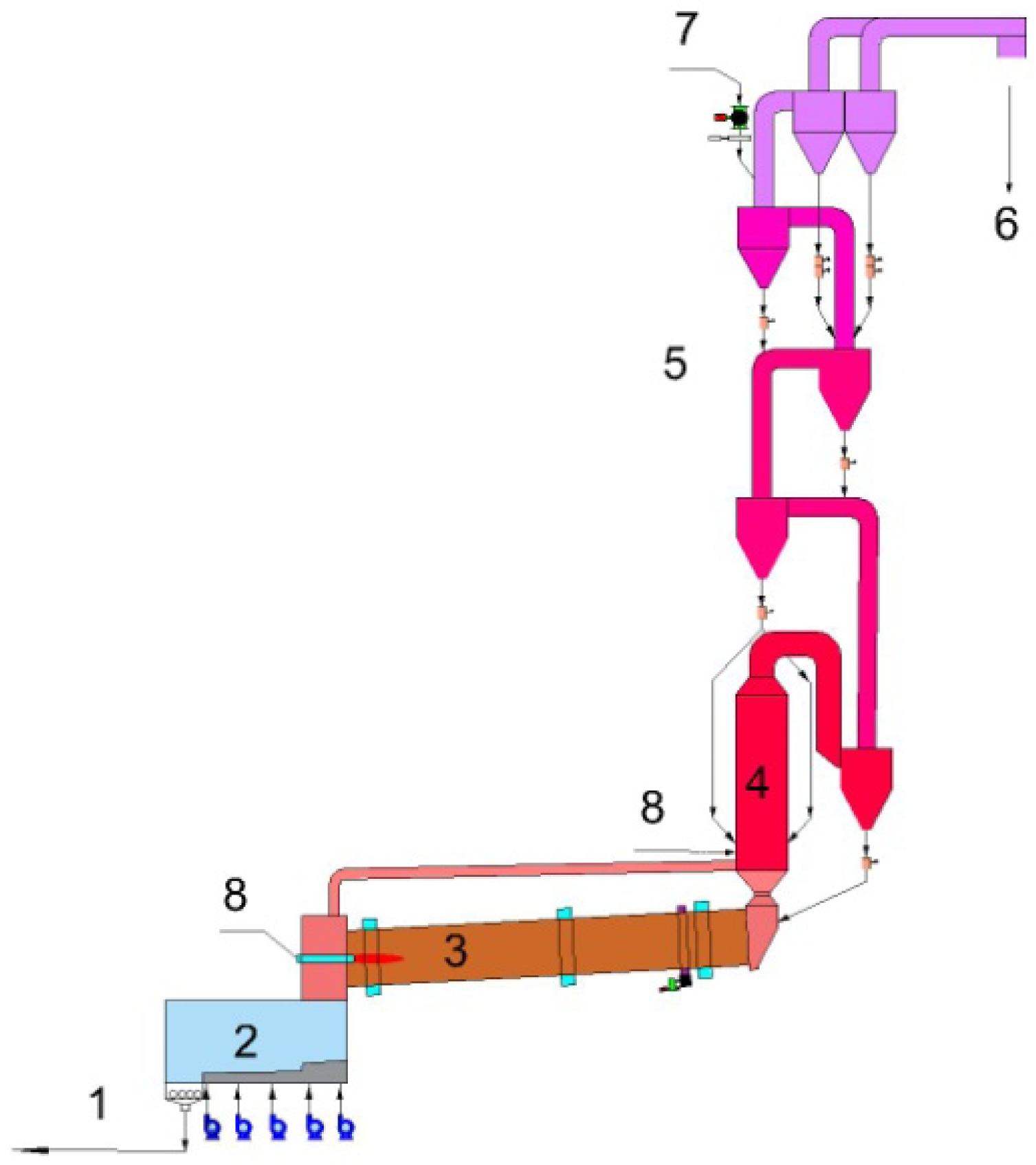
|
Fig. 1 Schematic view of clinker production in Portland cement industry. |
|
Table 1 Energy consumption level of different Portland cement calcining equipment. |
Gypsum initial decomposition temperature reaches 1662 ℃ by thermodynamic calculation, but the decomposition temperature decreases significantly in the presence of reducing agents, such as coke, sulfur, hydrogen or carbon monoxide, which the decomposition temperatures are 849, 1054, 909 and 925 ℃, respectively. Xiao et al. [11] discover that initial decomposition temperature of CaSO4 is 1246 ℃ in air atmosphere, and the end temperature is 1395 ℃, probably because of trace impurities in the gypsum can promote it decomposition. Coal, coke, sulfur, CH4, CO and H2 can all be used as reducing agents for gypsum decomposition. On the other hand, coal, coke and sulfur are a solid and easily stored and used in industry. Moreover, sulfur and H2 do not emit carbon dioxide and is environmentally friendly. The reducing agent can reduce the decomposition temperature of gypsum and increase the decomposition rate. Among these reducing agents, coal or coke (carbon) has a lower cost and is suitable for industrial application. The mechanism of carbon as reducing agent to decompose gypsum can divide into two types: solid-solid reaction mechanism and gas-solid reaction mechanism. It is generally believed that the reaction between gypsum and carbon are mainly solid-solid reaction in packing mode, and the gas-solid reaction is the main reaction in suspending mode [12].
Solid-solid reaction mechanism:
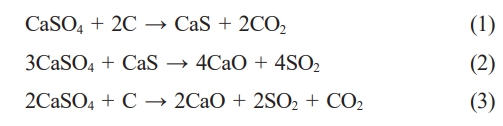
When the reaction temperature changes from low to high, the reaction equation (1) occurs first, following by the equation (2). The equation (3) can combine by the equation (1) and (2), which CaS is an intermediate product. In addition, under a strong reducing atmosphere, the final product only contains CaS. Zheng et al. [12] find that the reaction between CaS and CaSO4 (equation 2) can be completed by involving liquid intermediate phase, which use flue gas desulfurization (FGD) gypsum and anthracite as raw materials. Davies et al. [13] also find the presence of melt phases in the temperature range between 850 ℃ and 1000 ℃, which use CaS and CaSO4 (both 99% pure and 45-20 um in particle size) as raw materials. The presence of liquid phase promotes the reaction (2).
Gas-solid reaction mechanism:
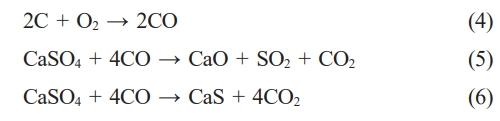
In fluidized bed suspending mode, the coal is oxidized to form CO gas, and then the CO reacts with gypsum to form calcium oxide, but CaS will be generated in a strong reducing atmosphere. When the CO concentration is 2%, the highest CaO content is 91.6% in the product [14].
There are many researches on the influent factors of the above reactions. In the research of gypsum decomposition into calcium sulfide, for example, Motaung et al. [15] find that heat treatment temperature plays an important role in the process of gypsum decomposition, which use gypsum (purity 95.54%) and bituminous coal produced by the neutralization of wastewater as raw materials. The CaS content increases with the increase of reduction temperature. The CaS content is low by heat treatment at 900 ℃ for 20 min. But the content of CaS is more than 80% by heat treatment at 1000, 1050 and 1100 ℃ for 20 min, 15 min and 10 min, respectively. Jia et al. [16] find that CaSO4 is decomposed into CaS at 600-800 ℃ and CaO is no produced, which used gypsum (purity >97%) and coal as raw materials. The decomposition rate increases from 34.72% to 84.76% when the holding time ranges from 0 to 20 min at 800 ℃. The particle size of coal increases, the contact area between gypsum and coal decreases, and the reaction rate decreases. In addition, they also find that FeSO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 in coal can help CaSO4 to decompose, which iron can promote the decomposition. Further research is needed on the reaction kinetics.
In research on gypsum decomposition into calcium oxide, for example, Kato et al. [17] find the main phase is CaS when the carbon-sulfur ratio (C/S) is 0.5 and heat treatment temperature is 800-900 ℃, which use chemically pure gypsum and heavy putty (carbon source) as raw materials. CaSO4, CaS and CaO coexist in sample by heat treatment at 900 ℃. CaS disappears, only CaSO4 and CaO exist by heat treatment at 1000 ℃, which the CaO content is as high as 90%. In generally, the temperature of PG decomposion into CaO is 950-1200 ℃ by using different reducing agents [18]. In addition, impurities (e.g., SiO₂, Al₂O₃, Fe₂O₃) in gypsum, can react with gypsum to form Portland cement minerals, such as calcium silicate, calcium aluminate or calcium ferrite, etc., which can change the decomposition process of gypsum, reduce the decomposition temperature and obtain product with excellent performance, but the content of impurities must meets the chemical composition requirements of Portland cement. The Fe2O3 can inhibit the formation of CaS under the same reducing atmosphere, and the inhibition increases with the Fe2O3 addition amount increase, but the addition of SiO2 or Al2O3 has no obvious inhibitory effect on the formation of CaS [19].
According to above analysis, the decomposition of CaSO4 into CaS is easier than that into CaO. It is necessary to control the decomposition atmosphere to be a slightly reducing atmosphere [20]. However, firing clinkers needs in an oxidizing atmosphere. The reducing atmosphere affects the mineral composition and clinker color, shortens cement setting time, increases early hydration heat, and reduces soundness [21]. In addition, SO2 gas is easily reduced to sulfur in a reducing atmosphere, which sulfur causes the blockage of flue gas purification equipment, destroys electric demister, and affects sulfuric acid production [22, 23].
In some country, gypsum is decomposed in the rotary kiln, but it is difficult to control the atmosphere in the kiln, which high quality clinker cannot be produced. The technology of suspension preheater-circulating fluidized bed precalcining is not been widely reported and applied. According to limestone precalcining technology in Portland cement industry, the decomposition of gypsum is carried out in the furnace outside the kiln, which the furnace is a fixed equipment that can be connected to air or fuel at its different locations to control the reducing atmosphere inside the furnace. On the other hand, it is beneficial to control the atmosphere in the kiln, so the clinker can be calcined in an oxidizing atmosphere to obtain high quality cement.
Cement can be divided into high-calcium cement (eg, Portland cement and Alite cement) and low-calcium cement (eg, Belite cement, sulfoaluminate cement) according to the content of calcium oxide in the cement. High-calcium cement uses tricalcium silicate (3CaO·SiO2, C3S, mineral name: Alite) as the main mineral (50%-70%), and low-calcium cement contains more dicalcium silicate (2CaO·SiO2, C2S, mineral name: Belite, ≥30%). The formation enthalpy of C3S mineral is 1810 kJ/kg, and the formation temperature is as high as 1450 ℃, while the formation enthalpy of C2S mineral is only 1350 kJ/kg, which can be formed at 1300 ℃. Reducing the content of C3S mineral and increasing the content of C2S mineral can reduce the energy consumption of cement clinker [24]. However, C2S has slow hydration rate and low early strength. Low calcium cement, such as sulfoaluminate cement and belite sulfoaluminate cement, are produced by introducing a early-strength mineral (calcium sulfoaluminate) into the clinker.
In addition, PG contains two impurities, eg. phosphate and fluoride. Phosphate can hinder the formation of C3S and affects clinker strength. Fluoride reduces the melting point of clinker, and it is easy to form scales in kiln, which scales affect high quality clinker to produce [25]. On the other hand, in order to reduce the content of harmful impurities in PG, phosphorus and fluorine can be removed by water washing or flotation processes. In order to obtain high quality clinker, PG without the impurities is necessary, but it affects the co-production process application [26, 27].
In order to reduce the calcined temperature and avoid the influence of impurities on clinker, some researchers have prepared low calcium cement containing sulfoaluminate mineral.
Sulfoaluminate cement (calcium sulfoaluminate, CSA) is anhydrous calcium sulfoaluminate (3CaO·3Al2O3·CaSO4, C4A3S¯ , mineral name: Ye'elimite) and dicalcium silicate (mineral name: Belite) as the main minerals. Compared with Portland cement, sulfoaluminate cement has some advantages, with low synthesis temperature (low 200 ℃), low calcium content, fast hydration reaction, high early strength, and micro-expansion, which has been applied as cement materials and repair materials [28]. Wu et al. [29] prepare CSA cement by using solid waste as raw materials (such as FGD gypsum, alumina slag, red mud, and fly ash). The cement has the highest strength by heat at 1310 ℃ for 60 min, with strength 63.3, 85.3, and 102.8 MPa for 1, 3, and 28 days, respectively.
The production and application of CSA cement will be limited because of the sources and price of high-alumina raw materials, and strength deterioration in long-term. Therefore, Belitt-calcium sulfoaluminate (BCSA) cement, with reduced C4A3S¯ content and increased C2S content, has received more and more attention. Huang et al. [30] prepare BCSA cement clinker with PG and bauxite as raw materials, which PG is also used as a retarder for BCSA cemen. They research the effects of P2O5 and F impurities in PG on clinker formation and cement hydration. The P2O5 and F impurities in PG can promote the formation of clinker and the BCSA clinker can be obtained by heat at 1200 ℃, which the calcination temperature is 50 ℃ lower than that obtained with natural gypsum (NG). P2O5 and F can be solid-dissolved in C4A3S¯ and make the C4A3S¯ mineral to form a cubic crystal, resulting in a decrease in the hydration activity of C4A3S¯ . But the impurities have little effect on the cement compressive strength. The compressive strength of BCSA cement can reach 70 MPa at 28 d age. When PG is used as the retarder of the BCSA cement, the soluble phosphorus impurity inhibits the hydration of C4A3S¯ and prolongs the cement initial and final setting time with 6-12min. And the delay of setting time is beneficial to cement construction, which reduces the cement early compressive strength but does not affect the strength at 28d.
In addition, Skalamprinos et al. [31] prepare single-phase calcium sulfosilicate at 1175 ℃. The compressive strengths of the samples are 30 and 65 MPa by curing at 25 ℃ for 28 and 90 d, respectively, which the hydration products are CSH and plaster. Huang Y et al. [30] prepare calcium sulfoaluminate cement by the partial substitution of Al for Fe in C4A3S¯ (C4A3-xFxS¯ exceeds 0.7). For the iron rich CSA cement, the setting time is prolonged and the expansion rate lowers down with the rise of Fe2O3 content. For the compressive strengths, the iron rich CSA cements are lower than that of CSA cement at early age. However, the compressive strength of iron rich CSA cement (~75 MPa) exceeds that of CSA cement (~65 MPa) at 90 d. Yang et al. [33] prepare belite-calcium aluminate ferrite cement at 1250 ℃ for 60 min by using PG, pyrite slag and bauxite as raw materials, which cement main phases are C4A3S¯ , C2S and C2AxF1-x (calcium iron aluminate). The compressive strength is about 48 MPa by curing at 20 ℃ for 3 d.
Moreover, small particles are beneficial for PG to produce cement. According to experience in the Portland cement industry, the raw material particle size should be reduced to less than 80 μm.
When the PG contains more silica, the cost of alumina raw materials is high and the durability of cement is required, high-strength-low-calcium Portland (LCP) cement will be the preferred for PG utilization. LCP cement mineral compositions and performance requirements are C2S ≥ 40%, compressive strength ≥ 17 MPa at 3 d, compressive strength≥52.5 MPa at 28 d, dry shrinkage ≤ 0.08% at 28 d and sulfate resistance (linear expansion rate ≤ 0.060% for 14 d) [23, 34]. In general, Portland cement clinker is an aggregate of multi-mineral complex phases, and the strength of clinker is mainly determined by the strength of four main minerals (tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, calcium aluminate and tetracalcium ferric aluminate). The clinker strength is not a simple sum of the four single minerals and it is a certain promotion between the minerals. The influence of clinker mineral and raw material composition on mineral calcination of LCP cement needs further in-depth research, while the cement can meet early strength requirements of construction.
In the different crystal structures of C2S, the hydration activity order from high to low are α-C2S, αH′-C2S, αL′-C2S, β-C2S and γ-C2S, which γ-C2S is the normal temperature phase and does not has binder property [35]. Moreover, there are two other structures, an amorphous structure with same chemical composition as the crystal, another X-C2S crystal, which the hydration activity of the two structures are higher than that of tricalcium silicate. At present, the methods to improve hydration activity of dicalcium silicate mainly are regulating structure by external ions during firing stage, adding foreign ions into the water during the forming stage, carbonizing with CO2 in the curing period [36].
In the firing stage of C2S, the preparation of highly active C2S has been intensively studied by doping foreign ions to change its structure. For example, Val et al. [37] prepare dicalcium silicate (C2S) by using calcium carbonate and silicon oxide as raw materials, and prepare tricalcium phosphate (TCP) by using calcium hydrogen phosphate and calcium carbonate as raw materials, and then, the C2S and the TCP are mixed by 85 wt% C2S-15 wt% TCP, the mixture is pressed into tablets, αH´-dicalcium silicate cement is prepared by firing the tablets at 1500 ℃ for 3 h. Yu et al. [38] find that phosphorus can reduce the formation temperature of clinker minerals and inhibite the conversion of β-C2S to γ-C2S in the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system. In addition, nano-additives (eg. nano-TiO2 and nano-MgO) can stabilize β-C2S structure at room temperature [39].
Another way to improve C2S hydration activity is adding foreign ions into the molding water to change its liquid phase environment. Fami et al. [40] find that Belite dicalcium silicate (Ca2SiO4, β and α’) accelerate hydration by adding alkali (NaOH or KOH), and calcium silicate hydrate C-S-H phase of C-(N)-S-H sodium and C-(K)-S-H potassium form, which sodium and potassium are solidified in calcium silicate hydrate. Ashraf et al. [41] find that NaOH has the worst influence on γ-C2S activation in alkalis (Na2CO3, NaHCO3, Na2SiO3 and NaOH). The hydration reaction of γ-C2S activated by sodium hydroxide is about 50%, but the hydration reaction with other alkalis all reach more than 90% after age 56 days.
CO2 can enhance the hydration activity of C2S and improve its early strength [42]. For example, Mu et al. [43] find that γ-C2S has high carbonization reactivity because the Ca2+ ions dissolution rate increase in CO2 environment. The carbonized products is mainly calcite, and a little of aragonite and silica gel. The strength of the samples increases from 52.92 to 60 MPa by carbonization from 10 min to 120 min, which the carbonization increases matrix strength and surface density. Wang et al. [44] research the carbonization properties of pure minerals such as β-dicalcium silicate (β-C2S), calcium hydroxide (CH) and tetracalcium ferric aluminate (C4AF). They find that the carbonation degree of the minerals from large to small are as follows: CH > β-C2S > C4AF and the strength of the carbonization minerals are as follows: β-C2S > CH > C4AF. There are calcite particles in the carbonized β-C2S sample, with close packing and strong mechanical bonding, but there are obvious defects on the calcite particles in the carbonized C4AF sample. In addition, it will reduce the carbonization depth by adding slag in γ-C2S [45].
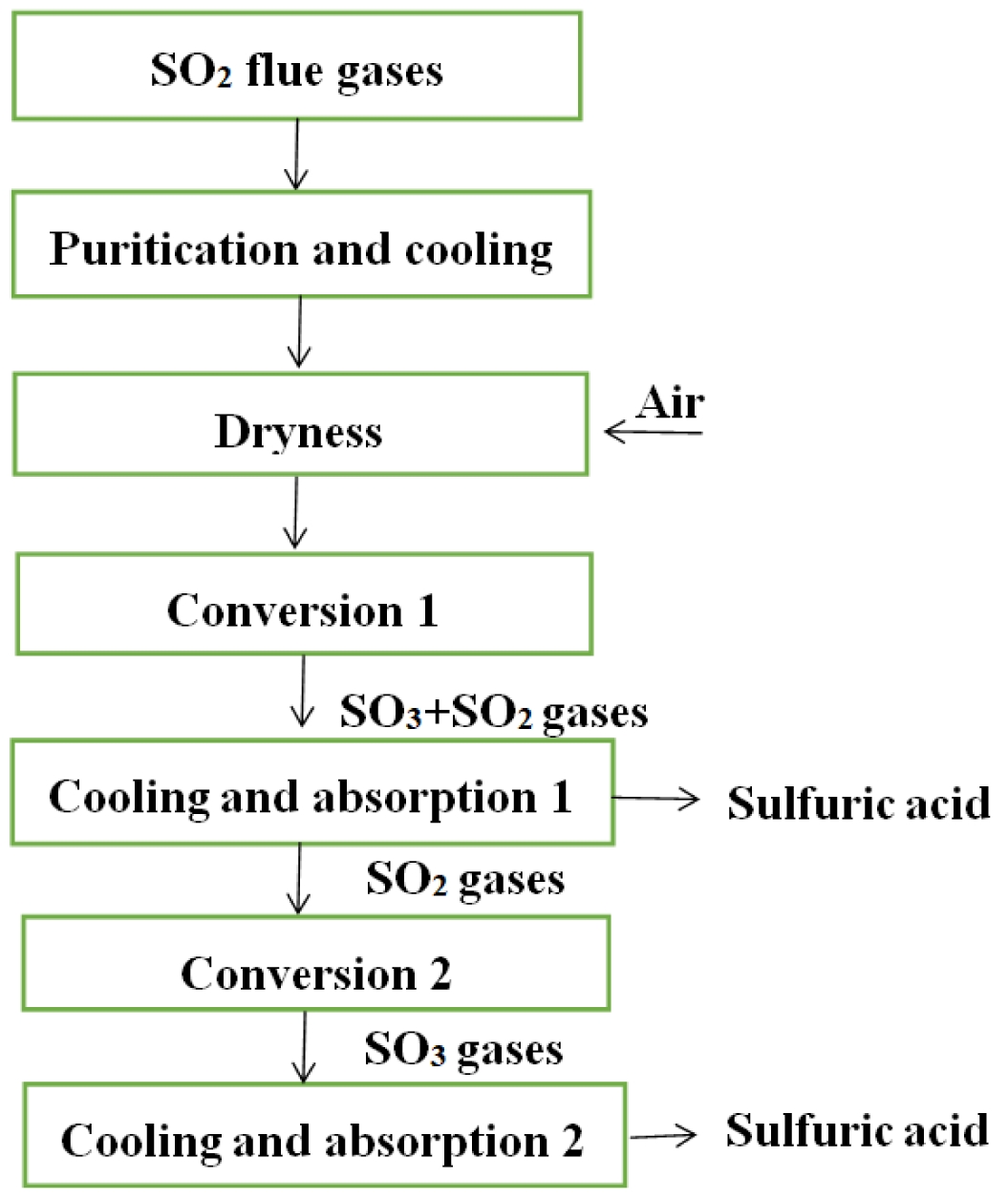
The sulphuric acid is produced from SO2 flue gases by purification, dry and conversion unit in acid manufacturing systems. The typical manufacturing process of sulphuric acid is shown in Fig. 2. On the other hand, wet gas sulfuric acid process is very well suited for industrial gases due to its ability to treat wet gases without additional drying steps [46].
Purification: Firstly, flue gases from cyclone preheating systems are removed raw materials powder by an electric precipitator. Secondly, the gases (about 300 ℃) are washed with 8%-10% dilute sulfuric acid and cooled (to about 60 ℃) in a cooling tower (empty tower). Thirdly, the washed gases are washed again with about 1.5% dilute sulfuric acid in a filled tower to further remove dust, fluorine and other impurities in the flue gases. Finally, the gases enter a drying tower after the acid mist is removed by the electric demister.
Dry: The drying tower is a filled tower, and a sulfuric acid (94.5 wt%) is sprayed on the top to absorb the water in the gases. The content of water is less than 0.1 g/m3 in the gases, and then, it enters the conversion section.
Conversion: The dried SO2 gases react with air gas in a converter (1-3 fixed adiabatic beds), which conversion rate can reach 93%. The SO3 and SO2 mixed gases enter the intermediate drying absorption tower after being cooled to 180 ℃. The residual SO2 gases from the absorption tower are heated to 410 ℃ by the heat exchanger and enter another converter for the second conversion. After the secondary conversion, the total conversion rate of SO2 can reach 99.5%, and after secondary absorption, the total absorption rate of SO3 can reach 99.95%.
Wu et al. [47] prepared calcium sulfoaluminate cement by using the decomposition of industrial by-product gypsum, and the concentration of SO2 could reach 7.55% thereby meeting the required concentration for the preparation of sulfuric acid. According to the results, the SO2 concentration also can reach the requirement when LCP cement is produced by using PG.
|
Fig. 2 the typical manufacturing process of sulphuric acid. |
Since cement production is a complex process that uses enormous amounts of raw materials and energy, it is important to evaluate its environmental impact and investigate how the industry should follow best practices. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a valuable method for assessing the environmental impacts of cement production [48].
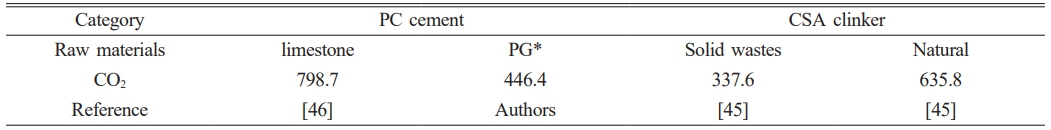
Ren et al. [49] prepared CSA clinker from red mud, desulfurization gypsum, and other industrial solid wastes, and the results were compared with a standard production method. The found that 635.8 Kg of CO2 were produced per tonne of cement clinker, including raw materials and fossil fuels processing, electricity production, transportation, and atmospheric emissions from the kiln for conventional CSA preparation, but only 337.6 Kg of CO2 were released when using industrial solid wastes to produce 1 tonne of clinker. Li et al. [50] give detailed LCA study for Portland cement (PC), which 798.7 Kg of CO2 were produced per tonne of cement. According to the calculation method of conventional PC, the CO2 emission is 446.4 Kg per tonne cement by using PG, including raw materials (for example, PG dehydration) and fossil fuels processing, electricity production, and atmospheric emissions. Greenhouse gas emission results of different cement/clinker are shown in Table 2.
In summary, the co-production process of PC cement and sulfuric acid using PG gypsum decomposition is more environmentally friendly [51]. The co-preparation of LCP cement and sulfuric acid using PG decomposition is a novel production process. Further research is needed to continue to define the LCA dependencies.
|
Table 2 The greenhouse gas emission results of different cement (kg/t). |
*The PG contains about 15 wt% adsorbed water. |
According to the mechanism of gypsum decomposition, the decomposition temperature will reduce by using coal as a reducing agent, which will help reduce energy consumption. When the PG contains more silica, the cost of alumina raw materials is high and the durability of cement is required, high-strength-low-calcium Portland cement will be the preferred for PG utilization.
According to limestone precalcining technology in Portland cement industry, the decomposition of gypsum is carried out in the furnace outside the kiln and clinker is calcined in the kiln. The high concentration of sulfur dioxide in the flue gas (SO2 ≥ 10 vol%) can be generated by using oxygen enriched burning technology, which is beneficial for acid production from flue gas and sulfur recovery. High performance clinker can be produced by quality calcining technology to reduce the residence time of clinker in kiln. Further research is needed to continue to define these dependencies.
The methods to improve the activity of dicalcium silicate are still limited by external ions during firing stage and adding foreign ions into the water during the forming stage. High-strength-low-calcium Portland cement uses C2S as the main mineral, but the hydration activity of C2S is poor, and how to improve the activity will be further research. Moreover, C2S hydration rate can be promoted by carbonization in the curing period, but the carbonization efficiency, the microstructure and durability of carbonization products, etc., still need to be further research.
The co-preparation of LCP cement and sulfuric acid using PG is more environmentally friendly. Further research is needed to continue to define the LCA dependencies.
This work was supported by the Research Fund of the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2025ZDZX0019), Mianyang Science and Technology Program (2025ZYDF027) and Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry of Education (20kfgk01, 21kfgk01).
- 1. H. Tan, F. Dong, J. Liu, J. Wang, and X. He, Mater. Tehnol. 52[5] (2018) 633-637.
-

- 2. Y. Taha, A. Elghali, R. Hakkou, and M. Benzaazoua, Minerals 11[11] (2021) 1250.
-

- 3. H. Tan, A. Zheng, X. Kang, A. Jiang, W. Fang, Y. Liu, J. Li, X. He, and J. Liu, Mater. Tehnol. 54[5] (2020) 697-703.
-

- 4. C. Liu, L. Wang, H. Tan, F. Dong, X. Ma, and F. Yang, J. Ceram. Process. Res. 23[6] (2022) 778-782.
-

- 5. F. Costa and D. Ribeiro, J. Cleaner Prod. 276 (2020) 123302.
-

- 6. Y. Zhao, X. Yue, Y. Tang, X. An, and X. Shang, J. Ceram. Process. Res. 25[5] (2024) 862-870.
-

- 7. A. Saxena, A. Abraham, and B. Sang, J. Ceram. Process. Res. 25[6] (2024) 1122-1141.
-

- 8. O. Ige, O. Olanrewaju, K. Duffy, and C. Obiora, J. Cleaner Prod. 324 (2021) 129213.
-

- 9. S. Wu, Y. Yao, X. Yao, C. Ren, J. Li, D. Xu, and W. Wang, J. Cleaner Prod. 265 (2020) 121801.
-

- 10. H. Mikulčić, J. Klemeš, M. Vujanović, K. Urbaniec, and N. Duić, J. Cleaner Prod. 136 (2016) 119-132.
-

- 11. H. Xiao, J. Zhou, X. Cao, H. Fan, L. Fang, and K. Zhen, Power Engineering 24[6] (2004) 889-892.
- 12. S. Zheng, P. Ning, L. Ma, F. Cheng, and J. Shi, Combust Sci. Technol. 186[3] (2014) 377-386.
-

- 13. N. Dvaies and A. Hyahurst, Combust. Flame [106] (1996) 359-362.
-

- 14. Z. Miao, H. Yang, Y. Wu, H. Zhang, and X. Zhang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. [51] (2012) 5419-5423.
-

- 15. S. Motaung, J. Zvimba, J. Maree, and A Kolesnikov, Water SA 41[3] (2015) 369-374.
-

- 16. X. Jia, Q. Wang, K. Cen, and L. Chen, Fuel 163 (2016) 157-165.
-

- 17. T. Kato, K. Murakami, and K. Sugawara, Chem. Eng. Trans 29 (2012) 805-810.
-

- 18. Y. Wang, T. Wan, Y. Zhong, X. Ma, Z. Chen, and X. Wang, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim 139 (2020) 3457-3471.
-

- 19. N. Mihara, D. Kuchar, Y. Kojima, and H. Matsuda, J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag 9 (2007) 21-26.
-

- 20. L. Meng, Z. Ji, and J. Chen, Chem. Eng. Prog 36[2] (2017) 626-633.
- 21. K. Masaki, M. Suzuki, and I. Maki, Ceramic Transactions (1994) 3-17.
- 22. T. Feng, S. Zhang, J. Li, X. Xia, L. Li, X. Zhao, and C. Ma, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45 (2020) 20120-20131.
-

- 23. Q. Zhang, D. Lana, K. Chuang, and H. Wang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39[7] (2000) 2505-2509.
-

- 24. S. Liu, L. Wei, S. Zhou, X. Guan, and L. Wang, Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 33[3] (2014) 553-557.
- 25. L. Huang and Z. Yang, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim 138 (2019) 973-981.
-

- 26. P. Fang and S Liu, Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 38[8] (2019) 2430-3434.
- 27. Z. Yang, Q. Chen, and Q. Guo,Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 35[9] (2016) 2860-2865.
- 28. L. Xu, K. Wu, N. Li, X. Zhou, and P. Wang, J. Cleaner Prod. 161 (2017) 803-811.
-

- 29. S. Wu, W. Wang, C. Ren, X. Yao, Y. Yao, Q. Zhang, and Z. Li, Constr. Build. Mater 228 (2019) 116137.
-

- 30. Y. Huang, J. Qian, X. Kang, J. Yu, Y. Fan, Y. Dong, W. Zhang, and S. Wang, Constr. Build. Mater 203 (2019) 432-442.
-

- 31. S. Skalamprinos, G. Jen, I. Galan, M. Whittaker, A. Elhoweris, and F. Glasser, Cem. Concr. Res 113 (2018) 27-40.
-

- 32. Y. Huang, Y. Pei, J. Qian, X. Gao, J. Liang, G. Duan, P. Zhao, L. Lu, and X. Cheng, Constr. Build. Mater 249 (2020) 118774.
-

- 33. L. Yang, Y. Yan, Z. Hu, and X. Xie, Constr. Build. Mater 38 (2013) 8-13.
-

- 34. Y. Liu and L. Wang, New Building Materials 11[7] (2015) 10-13.
- 35. A. S. Brand, J. M. Gorham, and J. W. Bullard, Cem. Concr. Res. 118 (2019) 69-83.
-

- 36. W. Zhang, J. Zhang, and J. Ye, J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 47[11] (2019) 1663-1669.
- 37. J. E. M. S deVal, J. L. Calvo-Guirado, J. M. G. Marin, G. G. Moreno, P. Mazon, and P. N. de Aza, Ceram. Int. 42[1] (2016) 952-960.
-

- 38. H. Yu, X. Pan, K. Dong, and Y. Wu, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29[3] (2019) 650-656.
-

- 39. S. Maiti and C. Ghoroi, Cem. Concr. Res. 98 (2017) 111-121.
-

- 40. N. Fami, H. Ez-zaki, A. Diouri, O. Sassi, and A. Boukhari, Constr. Build. Mater 247 (2020) 118589.
-

- 41. W. Ashraf, Constr. Build. Mater 185 (2018) 617-627.
-

- 42. J. Chang, T. Jiang, and K. Cui, Constr. Build. Mater 312 (2021) 125359.
-

- 43. Y. Mu, Z. Liu, F. Wang, and X. Huang, Constr. Build. Mater 177 (2018) 322-331.
-

- 44. D. Wang and J. Chang, Constr. Build. Mater 224 (2019) 336-347.
-

- 45. Z. X. Chen, S. H. Chu, Y. S. Lee, and H. S. Lee, J. Cleaner Prod. 262 (2020) 121385.
-

- 46. P. Sørensen, M. Møllerhøj, and K. Christensen, Chem. Eng. J 278 (2015) 421-429.
-

- 47. S. Wu, Y. Yao, X. Yao, C. Ren, J. Li, D. Xu, and W. Wang, J. Cleaner Prod. 265 (2020) 121801.
-

- 48. O. Ige, O. Olanrewaju, K. Duffy, and C. Obiora, J. Cleaner Prod. 324 (2021) 129213.
-

- 49. C. Ren, W. Wang, Y. Mao, X. Yuan, Z. Song, J. Sun, and X. Zhao, J. Cleaner Prod. 167 (2017) 1314-1324.
-

- 50. C. Li, S. Cui, Z. Nie, X. Gong, Z. Wang, and N. Itsubo, Int. J. Life Cycle Assess 20 (2015) 117-127.
-

- 51. C. Mo, W. Liao, B. Liang, and C. Li, CIESC Journal 68[6] (2017) 2501-2509.
 This Article
This Article
-
2025; 26(6): 1104-1110
Published on Dec 31, 2025
- 10.36410/jcpr.2025.26.6.1104
- Received on May 20, 2025
- Revised on Oct 29, 2025
- Accepted on Oct 30, 2025
 Services
Services
- Abstract
introduction
current status of the co-production progress in industry
research progress of gypsum decomposition
research progress of low-calcium cement containing sulfoaluminate
research progress of high-strength-low-calcium portland cement
production process of sulphuric acid from so2flue gas
life cycle assessment of the co-production progress
conclusion and outlook
- Acknowledgements
- References
- Full Text PDF
Shared
 Correspondence to
Correspondence to
- Hongbin Tan
-
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China
Tel / Fax: +86 816 2419201 - E-mail: hb-t@163.com






 Copyright 2019 International Orgranization for Ceramic Processing. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2019 International Orgranization for Ceramic Processing. All rights reserved.